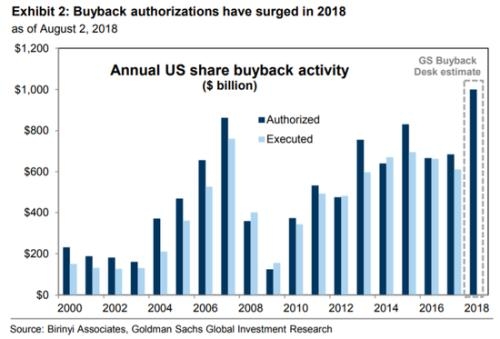
In the world of corporate finance, the treatment of stock compensation has been a hot topic for years. The question of whether or not to expense stock compensation is one that companies grapple with regularly. This article delves into the nuances of this issue, exploring the potential impacts on financial statements and corporate decision-making.
Understanding Stock Compensation
Stock compensation refers to the granting of equity awards to employees as part of their compensation package. These awards can take various forms, such as stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or performance shares. The key question is whether these awards should be expensed on the company's financial statements.
The Argument for Expensing Stock Compensation
Proponents of expensing stock compensation argue that it provides a more accurate representation of a company's financial performance. By recognizing the cost of stock compensation in the income statement, companies can provide investors and stakeholders with a clearer picture of their profitability.
The Argument Against Expensing Stock Compensation
On the other hand, critics of expensing stock compensation argue that it can artificially deflate earnings. They contend that the expense may not reflect the true economic value of the equity awards, as it is difficult to predict the future value of the shares granted.
Financial Statement Implications
Expensing stock compensation can have a significant impact on a company's financial statements. By recognizing the expense, companies may see a decrease in their net income and earnings per share. This can affect key financial ratios, such as return on equity (ROE) and price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios.
Case Study: Apple
A notable example of the debate over stock compensation is the case of Apple Inc. In 2012, Apple changed its accounting policy to expense stock compensation, which resulted in a decrease in its net income. The company cited the need for greater transparency and a more accurate reflection of its financial performance.
Case Study: Google
In contrast, Google has chosen not to expense stock compensation. The company argues that the expense would not provide meaningful insights into its financial performance, as it focuses on long-term value creation rather than short-term earnings.
Considerations for Companies
When deciding whether or not to expense stock compensation, companies should consider several factors:
- Regulatory Requirements: Different jurisdictions have different accounting standards for stock compensation. It is crucial to comply with the relevant regulations.
- Investor Expectations: Companies should consider how their decision will impact investor perceptions and market valuation.
- Strategic Objectives: The decision should align with the company's long-term strategic goals and compensation philosophy.
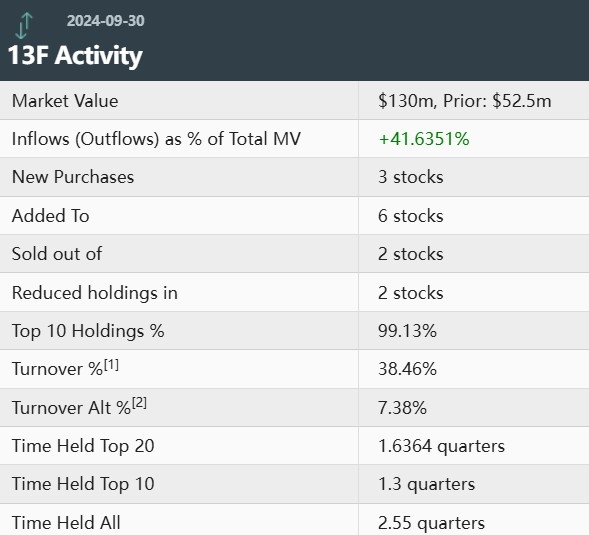
Conclusion
The question of whether or not to expense stock compensation is complex and depends on various factors. While expensing stock compensation can provide a more accurate reflection of a company's financial performance, it may also have negative implications for financial ratios and market valuation. Ultimately, companies should carefully consider the potential impacts and align their decision with their strategic objectives and regulatory requirements.
In-Depth Analysis of Reed's, Inc. Stoc? new york stock exchange