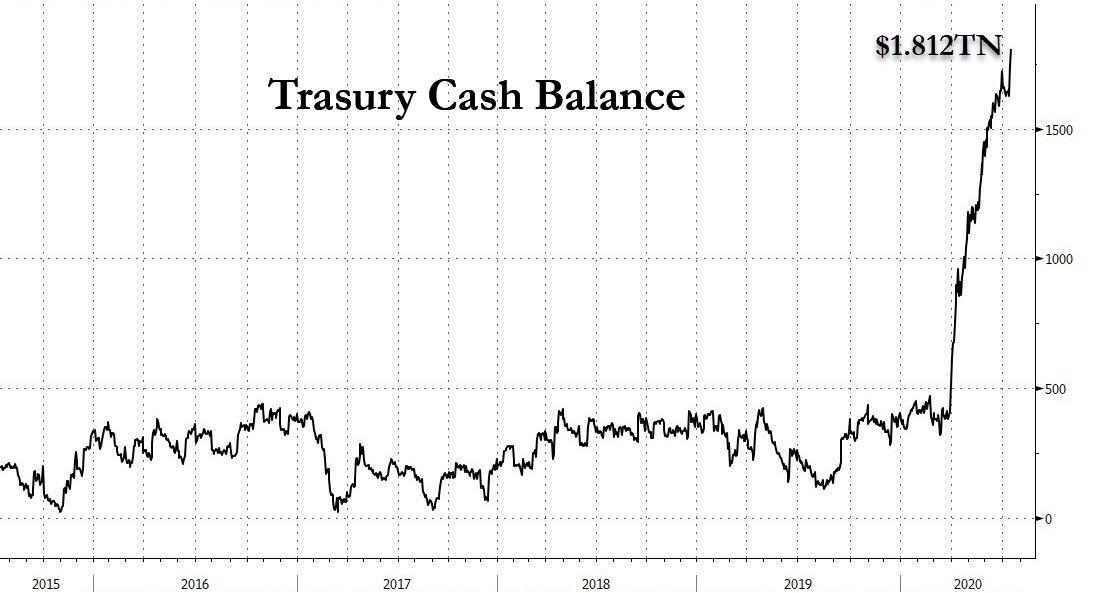
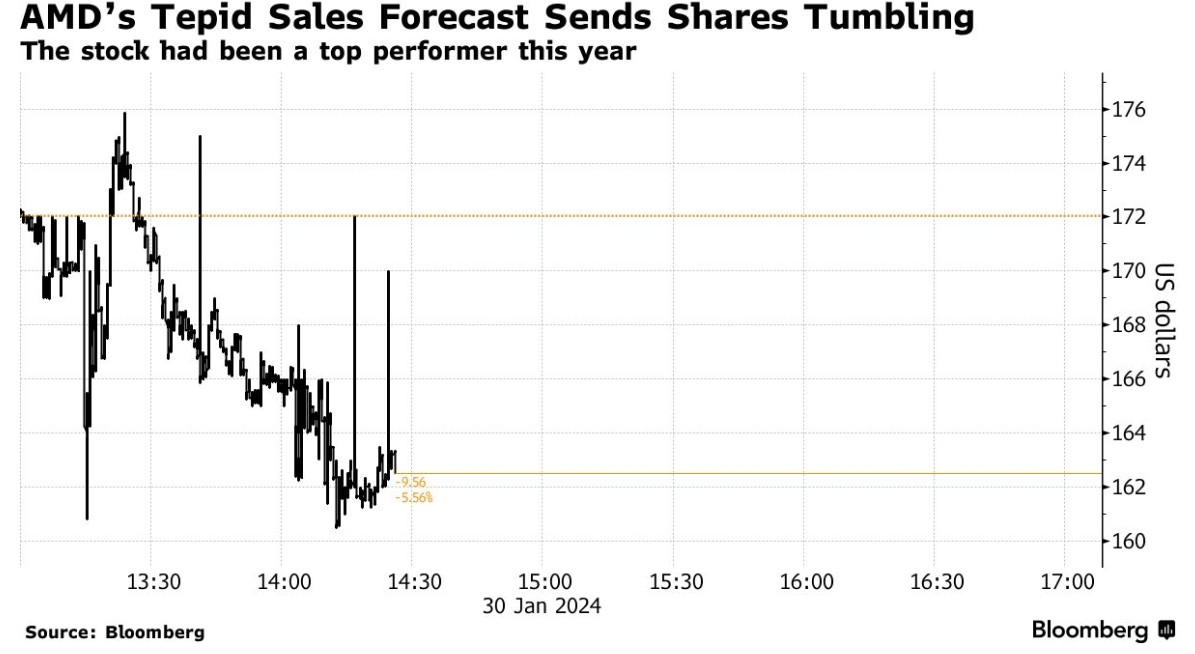
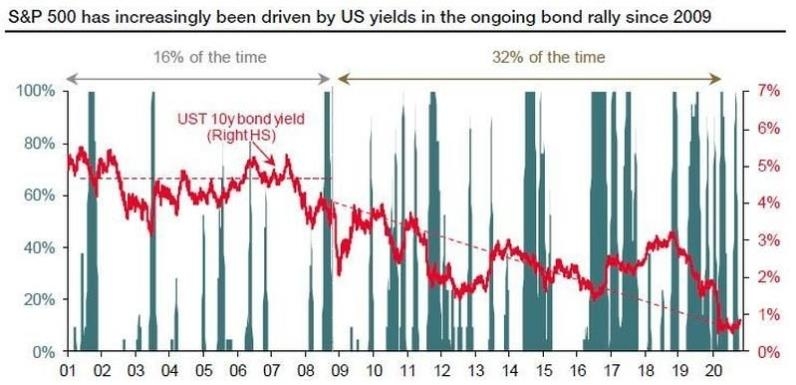
The S&P 500 has long been a benchmark for the health of the U.S. stock market. Over the past century, this index has seen numerous ups and downs, reflecting the economic cycles and shifts in the market landscape. In this article, we delve into a 100-year chart of the S&P 500, providing insights into its performance and the factors that have influenced it.
The S&P 500 Over the Decades
The 1920s: The Roaring Twenties
The 1920s were a period of rapid economic growth and prosperity. The S&P 500 saw significant gains during this decade, with the index rising by over 200%. However, this period was also marked by speculative bubbles and excessive leverage, which would eventually lead to the stock market crash of 1929.
The 1930s: The Great Depression
The stock market crash of 1929 sent the S&P 500 plummeting, and the index would not recover to its pre-crash levels until the late 1930s. The Great Depression was a period of extreme economic hardship, and the stock market reflected this with significant losses.
The 1940s: World War II and Post-War Recovery
World War II had a significant impact on the S&P 500. The index experienced volatility during the war years, but it began to recover in the post-war period. The 1940s saw the S&P 500 grow by nearly 50%, reflecting the economic recovery and the expansion of the U.S. economy.
The 1950s: The Baby Boom Era
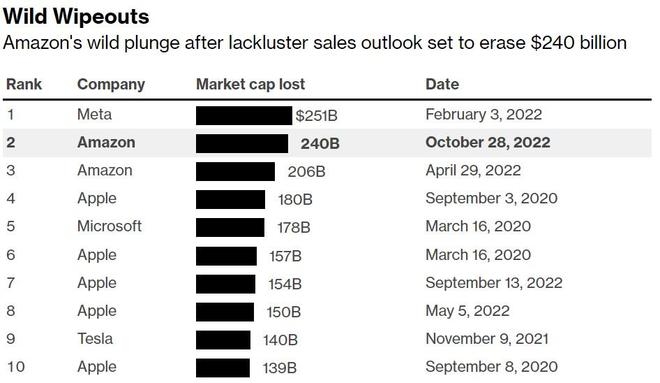
The 1950s were characterized by the post-war baby boom and the rise of consumer spending. The S&P 500 saw steady growth during this decade, with the index increasing by over 100%. This period was marked by technological advancements and the expansion of the middle class.
The 1960s: The Civil Rights Movement and the Vietnam War
The 1960s were a turbulent period in U.S. history. The Civil Rights Movement and the Vietnam War had a significant impact on the stock market, with the S&P 500 experiencing volatility. However, the index still managed to grow by over 50% during this decade.
The 1970s: The Oil Crisis and Inflation
The 1970s were marked by the oil crisis and high inflation. The S&P 500 experienced significant volatility during this decade, with the index rising and falling rapidly. However, the index still managed to grow by over 50%.
The 1980s: The Reagan Era
The 1980s were characterized by the Reagan administration's economic policies, which led to a period of low inflation and high growth. The S&P 500 saw significant gains during this decade, with the index increasing by over 200%.
The 1990s: The Dot-Com Bubble
The 1990s were marked by the dot-com bubble, which saw the S&P 500 reach record highs. However, the bubble burst in 2000, leading to a significant decline in the index. Despite this, the S&P 500 still managed to grow by over 50% during this decade.
The 2000s: The Financial Crisis
The 2000s were marked by the financial crisis of 2008, which had a devastating impact on the S&P 500. The index plummeted, but it eventually recovered and began to grow again.
The 2010s: A Decade of Recovery
The 2010s were characterized by a period of economic recovery. The S&P 500 saw significant gains during this decade, with the index increasing by over 100%.
Conclusion
The 100-year chart of the S&P 500 provides a comprehensive look at the performance of the U.S. stock market over the past century. While the index has experienced numerous ups and downs, it has generally trended upwards, reflecting the resilience of the U.S. economy and the stock market. By understanding the factors that have influenced the S&P 500 over the past century, investors can better navigate the market in the future.
The Evolution of the Dow Jones Industrial A? stock chap