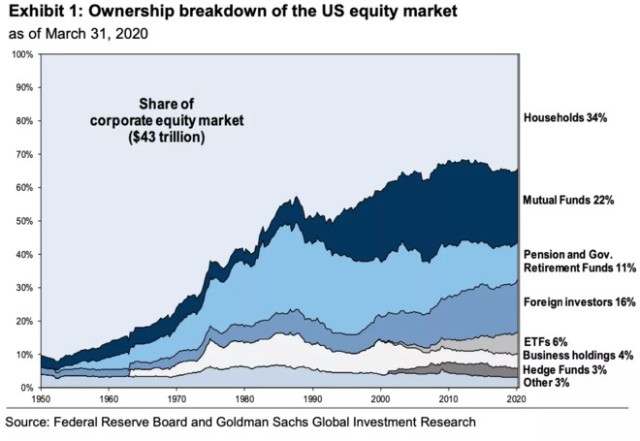
In today's interconnected global economy, the presence of foreign governments owning American stocks is a subject of significant interest. This article delves into the implications of this phenomenon, exploring the reasons behind it, the potential risks, and the broader economic landscape it reflects.
The Growing Trend
Over the past few decades, the ownership of U.S. stocks by foreign governments has surged. In fact, according to data from the U.S. Treasury, foreign governments now own more than $6 trillion in U.S. stocks. This figure includes investments from countries like China, Japan, and Saudi Arabia, among others.
Why Do Foreign Governments Invest in U.S. Stocks?
There are several key reasons why foreign governments invest in U.S. stocks:
- Economic Stability: The U.S. is often considered a safe haven for investors due to its strong economic fundamentals and political stability. This makes U.S. stocks an attractive investment for foreign governments looking to diversify their portfolios and protect their wealth.
- Economic Growth: The U.S. has been a leader in technological innovation and economic growth, making U.S. stocks a promising investment opportunity.
- Dollar Strength: As the world's primary reserve currency, the U.S. dollar remains strong, which benefits foreign investors who hold U.S. stocks.
The Risks
While investing in U.S. stocks can be lucrative, there are also risks associated with foreign governments owning them:
- National Security Concerns: Some critics argue that foreign governments owning U.S. stocks could pose national security risks. They fear that these governments could use their investments to gain undue influence over American businesses and policies.
- Economic Vulnerability: If foreign governments were to suddenly sell off their U.S. stockholdings, it could lead to a significant drop in the market and economic instability.
Case Studies
Several high-profile examples illustrate the impact of foreign governments owning U.S. stocks:
- China's Investments: China has been a major investor in U.S. stocks, with its holdings exceeding $1 trillion. This has raised concerns about China's economic and political influence in the U.S.
- Saudi Arabia's Purchase of Aramco: In 2019, Saudi Arabia purchased a majority stake in the U.S.-based oil company Aramco, which is one of the largest companies in the world.
Conclusion
The increasing ownership of U.S. stocks by foreign governments reflects the global interconnectedness of today's economy. While there are risks associated with this trend, the potential economic benefits are significant. Understanding the reasons behind this phenomenon and the potential risks is crucial for investors and policymakers alike.
Buying Swedish Stocks in the US: A Guide fo? stock chap