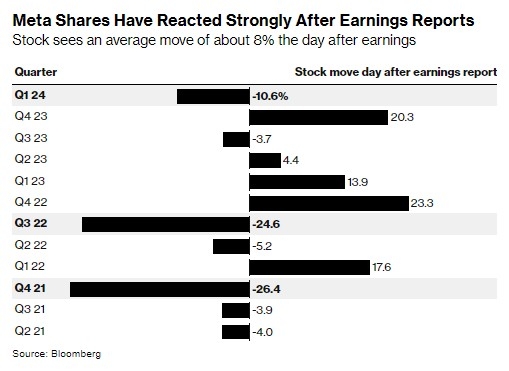
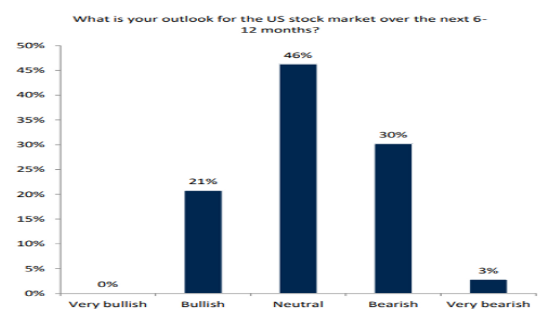
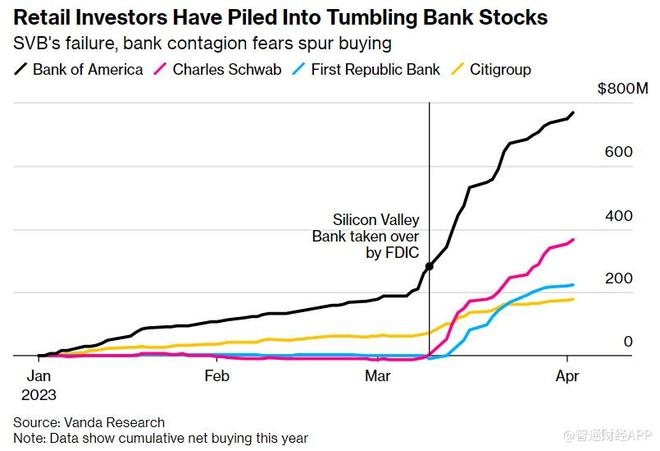
In the United States, the concept of a joint stock company has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation's economic and social landscape. This article delves into the definition of a joint stock company, its historical significance in the U.S., and how it has evolved over time.
What is a Joint Stock Company?
A joint stock company is a type of business entity where the capital is divided into shares, and investors purchase these shares to become part-owners of the company. The ownership is proportional to the number of shares they hold. This structure allows for the pooling of capital from multiple investors, making it easier for businesses to raise substantial funds for large-scale projects.
The Historical Context
The concept of joint stock companies originated in Europe during the 17th century. The first joint stock company, the Dutch East India Company (VOC), was established in 1602. The success of the VOC inspired other countries, including the United States, to establish their own joint stock companies.
Joint Stock Companies in U.S. History
The United States saw the emergence of joint stock companies during the colonial period and the early republic. One of the earliest examples was the Virginia Company (1606), which was chartered by King James I to establish settlements in North America. The Virginia Company raised capital through the sale of shares, allowing investors to participate in the potential profits from the new colonies.
Another significant joint stock company in U.S. history was the Bank of North America (1781), established by Alexander Hamilton. The bank played a crucial role in financing the American Revolutionary War and promoting economic development in the new nation.
Evolution of Joint Stock Companies
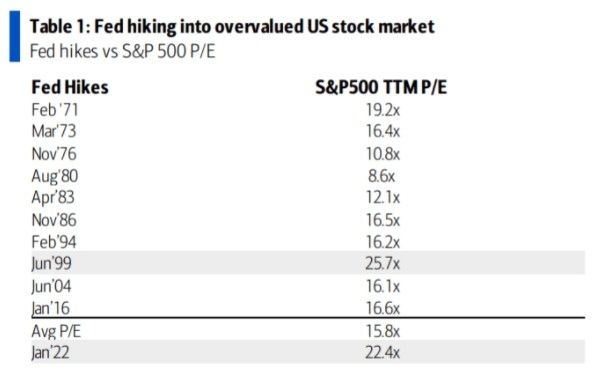
Over time, the definition and structure of joint stock companies have evolved. The Corporation Commission was established in the late 19th century to regulate the formation and operations of joint stock companies. This regulatory framework helped ensure that these entities operated in the best interest of their shareholders and the public.
In the 20th century, joint stock companies became more diverse, with the emergence of publicly traded companies. These companies offer shares to the public, allowing for wider participation in the ownership of large corporations.
Case Study: The Standard Oil Company
One of the most famous examples of a joint stock company in U.S. history is the Standard Oil Company. Established in 1870 by John D. Rockefeller, Standard Oil became the largest oil company in the world. The company's success was largely due to its innovative business practices, including the use of joint stock financing.
However, Standard Oil's monopoly over the oil industry raised concerns about antitrust laws. In 1911, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that Standard Oil was a monopoly and ordered it to be broken up into smaller companies. This decision marked a significant milestone in the regulation of joint stock companies in the United States.
Conclusion
The joint stock company has been a crucial component of the U.S. economy throughout its history. From the colonial period to the modern era, these entities have played a vital role in financing and promoting economic development. Understanding the definition and history of joint stock companies is essential for anyone interested in the evolution of the U.S. economy.
Dow Falls Today: What It Means for Investor? us flag stock