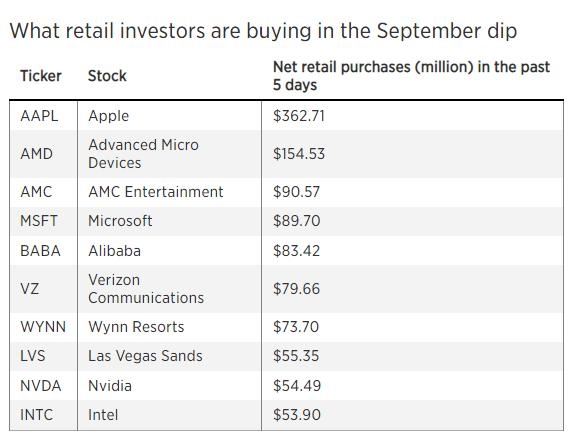
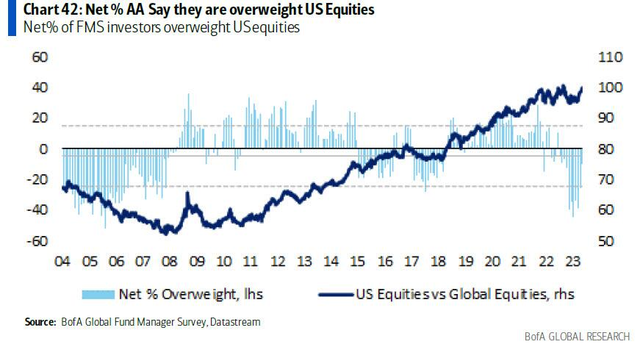
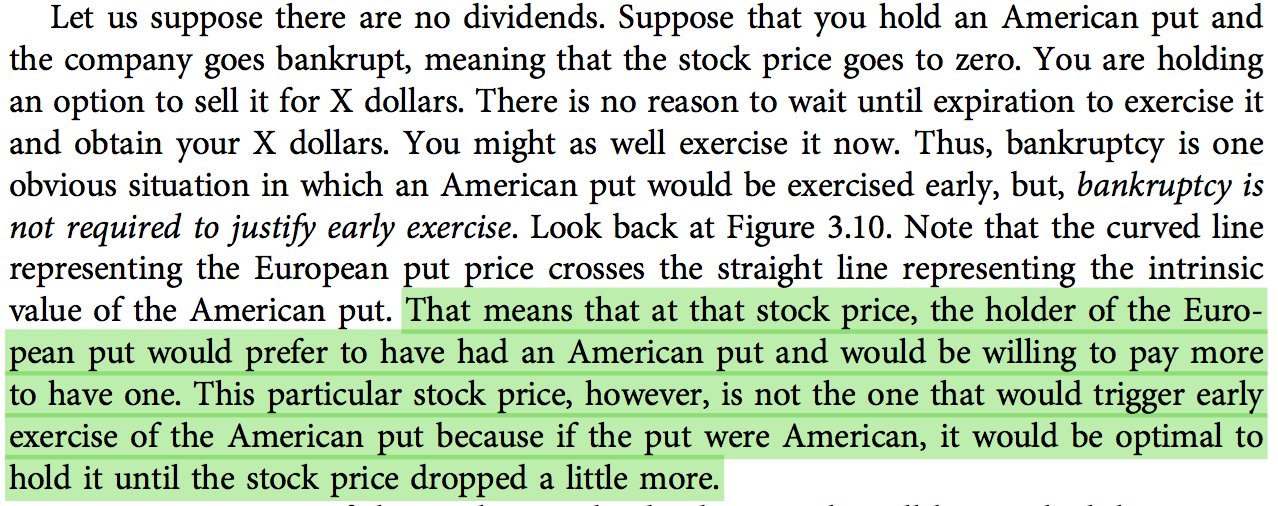
The 1929 stock market crash in the United States had profound repercussions that extended far beyond the borders of America, significantly affecting Europe's economy. This catastrophic event, often referred to as the "Great Crash," triggered a global economic downturn that lasted for years. This article delves into the ways in which the US stock market crash impacted Europe, analyzing the economic, political, and social consequences.
Economic Consequences
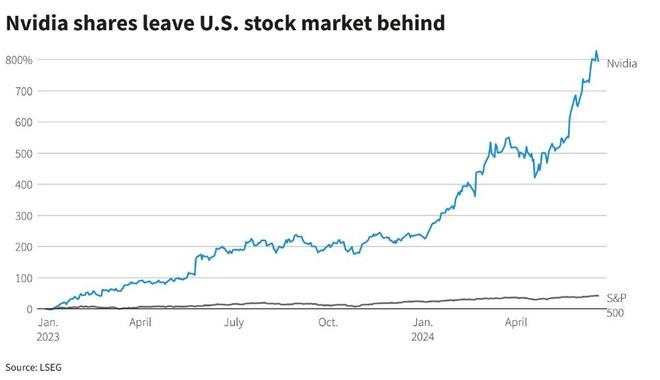
The direct impact of the crash on Europe was severe. Stock market values plummeted across the continent, leading to a loss of confidence in the financial system. Banks and businesses in Europe, which had significant investments in US stocks, faced liquidity crises and were unable to meet their obligations. This triggered a wave of bank failures and a depression in European economies.
Political Ramifications
The economic turmoil in Europe exacerbated political tensions and instability. In Germany, for example, the Great Depression deepened the country's economic problems, leading to the rise of the Nazi Party. The Hindenburg government, which was already struggling to deal with the economic crisis, collapsed in 1932, paving the way for the rise of Hitler and his authoritarian regime.
In Italy, the fascist government of Benito Mussolini faced increased pressure due to the economic crisis. The fascist regime used the crisis as an opportunity to consolidate its power, imposing strict economic controls and suppressing political opposition.
Social Impacts
The Great Depression had a devastating impact on European societies. Unemployment rates soared, leading to widespread poverty and homelessness. The social fabric of Europe was stretched to its limits, with hundreds of thousands of people losing their livelihoods and struggling to survive.
Case Studies
One notable case study is the impact of the stock market crash on the German economy. The crash led to a devaluation of the German mark and a sharp rise in inflation, which further exacerbated the country's economic problems. The hyperinflation that followed in the early 1920s led to the destruction of savings and a deepening of the economic crisis.
In France, the crash led to a reduction in consumer spending and a decline in industrial production. The government was forced to implement austerity measures, which further exacerbated the economic downturn.
Conclusion
The 1929 US stock market crash had far-reaching consequences for Europe, leading to economic, political, and social turmoil. The crash triggered a global economic downturn that lasted for years, and its impact is still felt today. By understanding the ways in which the crash affected Europe, we can gain valuable insights into the complexities of global economic relations and the interconnectedness of modern economies.
The Evolving Landscape: Number of Stocks on? us stock market today