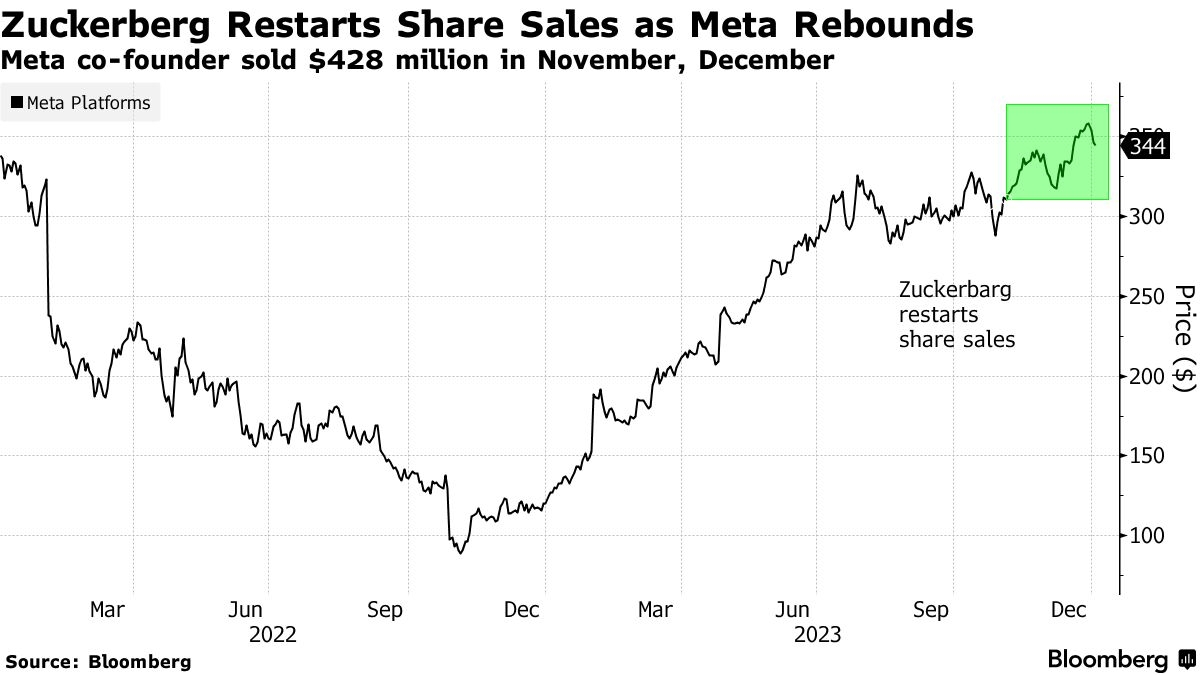
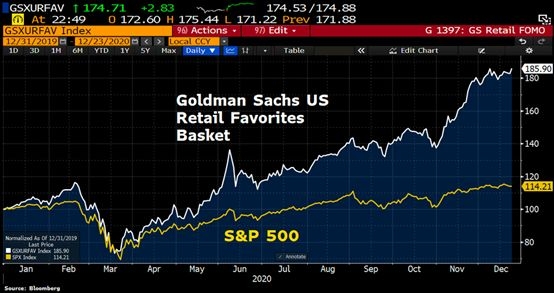
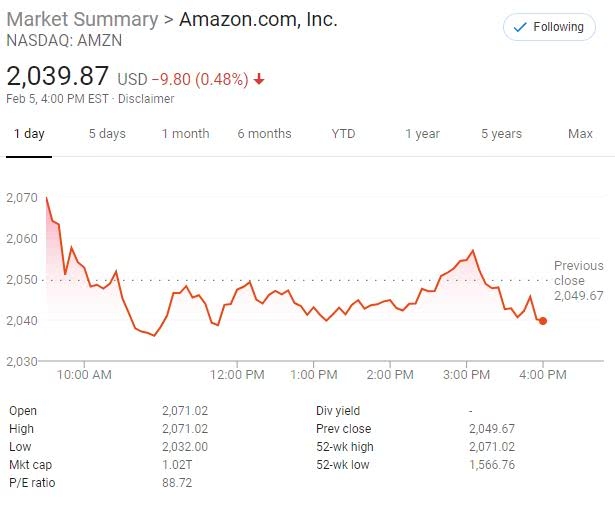
In the vast world of finance, the United States stock exchange market stands out as one of the most dynamic and influential. With a rich history and a robust structure, it has become a global benchmark for stock markets. This article delves into the intricacies of the US stock exchange market structure, providing an overview of its key components and their interplay.
The Primary and Secondary Markets
The US stock exchange market is divided into two primary markets: the primary market and the secondary market.
- Primary Market: This is where new securities, such as stocks and bonds, are issued for the first time. Companies go public through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) in the primary market. It's a crucial step that provides them with capital for expansion and operations.
- Secondary Market: Once a security is issued in the primary market, it is traded among investors in the secondary market. The most notable secondary market in the US is the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), followed by the NASDAQ.
Marketplaces and Their Roles
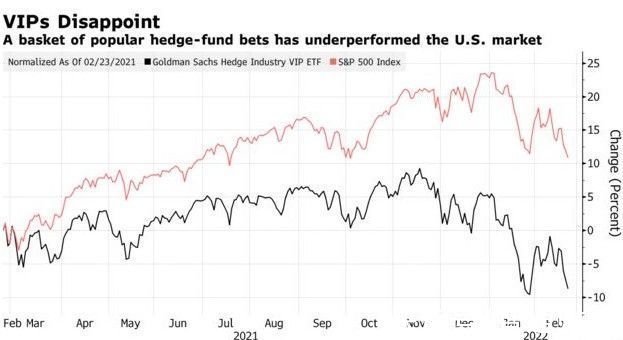
The US stock exchange market comprises several marketplaces, each with its unique characteristics:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): Established in 1792, the NYSE is the oldest and most iconic stock exchange in the world. It is a physical marketplace where traders buy and sell stocks through a series of auction-like processes. The NYSE lists a diverse range of companies, from major corporations to small-cap stocks.
- NASDAQ: The NASDAQ is a fully electronic marketplace that was established in 1971. It lists many technology companies and is known for its rapid trading speed and efficient order matching. Notable tech giants like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon are listed on the NASDAQ.
- AMEX: The American Stock Exchange, now known as NYSE American, is a smaller exchange that caters to smaller companies. It provides an alternative trading platform for companies looking to go public but may not meet the listing requirements of the NYSE or NASDAQ.
Regulatory Framework
The US stock exchange market operates under a stringent regulatory framework. The two key regulatory bodies are:
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): The SEC is responsible for regulating the securities industry, protecting investors, and ensuring fair and efficient markets.
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA): FINRA is a non-profit organization that regulates broker-dealers and exchanges. It aims to maintain fair and orderly markets and protect investors.
Key Features of the US Stock Exchange Market
- High Liquidity: The US stock exchange market is known for its high liquidity, making it easy for investors to buy and sell stocks.
- Market Capitalization: Companies are listed on the US stock exchange based on their market capitalization, which reflects their total value.
- Trading Hours: The NYSE and NASDAQ operate from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM Eastern Time.
Case Study: Apple Inc.
Apple Inc., a tech giant, went public on the NASDAQ in 1980. Since then, it has become one of the most valuable companies in the world. Its success story showcases the potential of the US stock exchange market for both companies and investors.
In conclusion, the US stock exchange market structure is a complex yet efficient system that facilitates the trading of securities. Understanding its various components and regulations is crucial for anyone interested in investing in the US stock market.
Daily US Stock Market Buy Recommendations: ? us stock market today