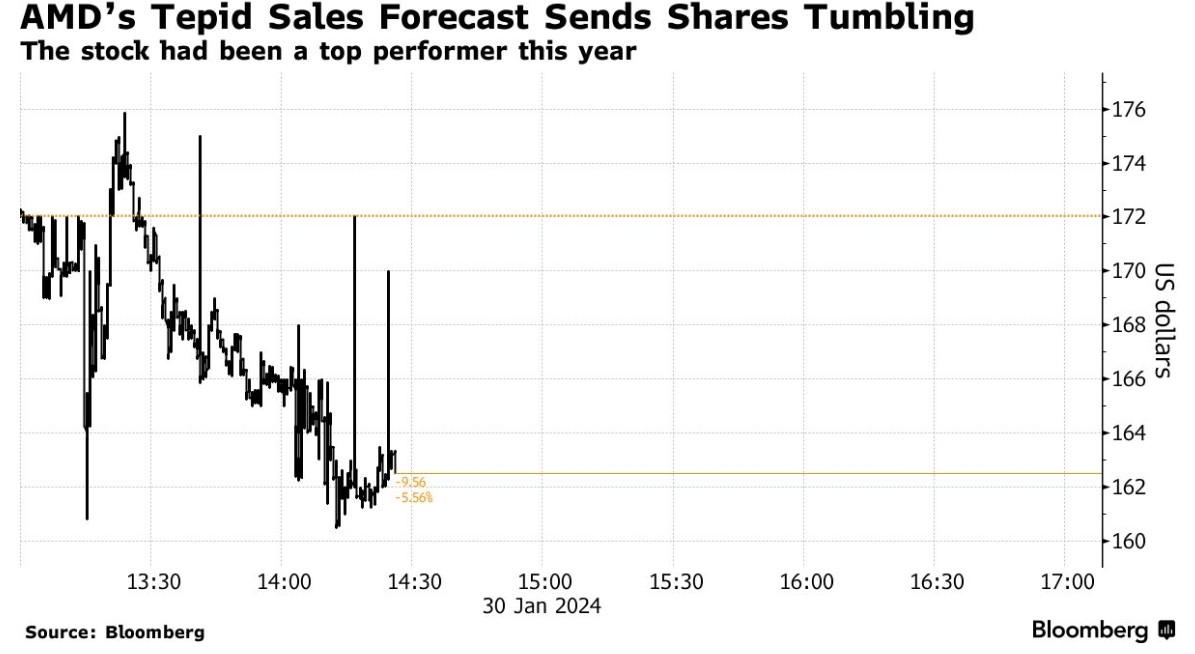
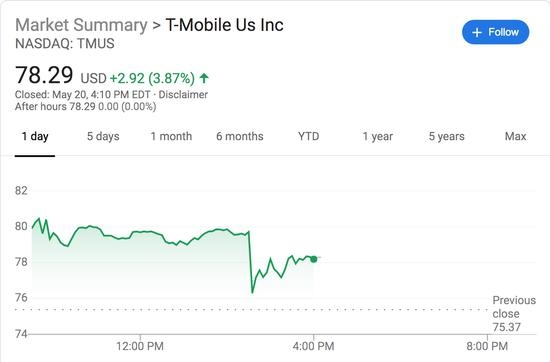
Investing in U.S. stocks can be a lucrative venture, but it's crucial for nonresident aliens to understand the tax implications. One of the most significant tax considerations is the nonresident alien US stock capital gains tax. This article delves into the details, providing clarity on how this tax affects foreign investors and what steps they can take to comply with U.S. tax regulations.
What is Nonresident Alien US Stock Capital Gains Tax?
The nonresident alien US stock capital gains tax refers to the tax imposed on the capital gains realized from the sale of U.S. stocks by nonresident aliens. This tax is governed by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and is designed to ensure that foreign investors pay their fair share of taxes on income earned from U.S. investments.
How is the Tax Calculated?
The tax rate for nonresident aliens on capital gains from U.S. stocks is generally 30%. However, this rate can be reduced under certain circumstances. For example, if the nonresident alien has a tax treaty with the United States, the tax rate may be lower.
The capital gains tax is calculated by subtracting the cost basis of the stock from the selling price. The cost basis includes the purchase price, any commissions paid, and any adjustments for dividends or other income received from the stock.
Exemptions and Exceptions
There are certain exemptions and exceptions to the nonresident alien US stock capital gains tax. For instance, if the nonresident alien holds the stock for more than a year, the gains may be taxed at a lower rate. Additionally, some gains may be exempt from tax if they are considered to be effectively connected income.
Reporting Requirements
Nonresident aliens must report their U.S. stock capital gains on Form 1040NR, the U.S. nonresident alien income tax return. This form requires detailed information about the stock transactions, including the date of purchase, date of sale, and the amount of gain.
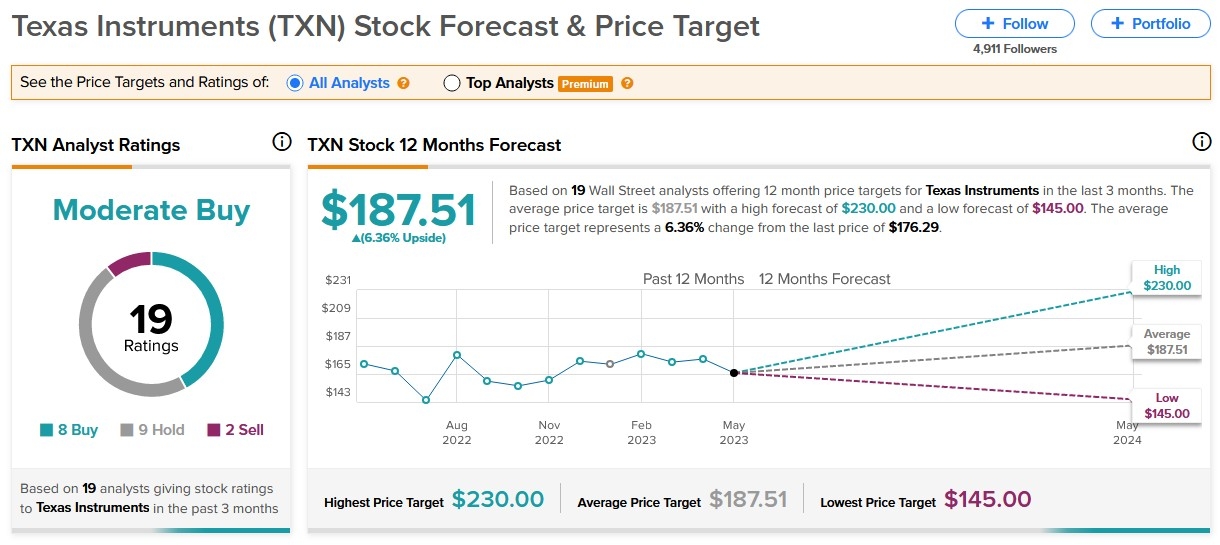
Case Study: John's U.S. Stock Sale
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario involving John, a nonresident alien. John purchased 100 shares of a U.S. stock for
Since John is a nonresident alien, he must pay a 30% tax on the gain, which amounts to $3,000. He would report this information on Form 1040NR and pay the tax accordingly.
Conclusion
Understanding the nonresident alien US stock capital gains tax is essential for foreign investors looking to invest in U.S. stocks. By familiarizing themselves with the tax regulations and reporting requirements, nonresident aliens can ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties. It's always advisable to consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with U.S. tax laws.
Understanding the US Healthcare Stock Index? us stock market today live cha